Transformational leadership has become important due to its ability to inspire and motivate employees during past decades. Transformational leadership not only helps organizations get employees’ contributions but also encourages them to care about the organization’s benefit beyond their personal interests. This leadership style has attracted considerable attention in the field of organizational behavior. This paper evaluates its impact on employee performance and motivation in medium-sized technology organizations. The tech industry faces several challenges like high speed of technology, high competition, and continuous need for innovation has different needs, leadership has an important role in these companies. The article presents the results of scientific research and findings from a survey conducted among employees in these organizations.
Understanding Transformational Leadership
Since 1973 when James MacGregor Burns (Burns 1978) started researching about Transformational Leadership until today, this topic has been extensively developed and much research occurred based on transformational leadership. In this article impacts of transformational leadership on the performance and motivation of employees will be asses. This research focused on Medium-sized companies in tech industry. Since the final product in tech companies are not tangible, we cannot assess the performance of the company like other industries. Using surveys as a tool helps this research to measure the most important factors in team performance and innovation.
The leader of a team plays a key role in the success of that team. Leaders play an important role in companies and employee performance by determining vision, strategy and using methods to increase employee motivation and participation. Transformational leadership develop a culture of ethical behavior and innovation. Effective leaders drive decision-making, manage change, and build stakeholder relationships, contributing to improved performance, adaptability, and resilience. They are essential in talent development and ensuring long-term sustainability and growth. The influence of leadership extends across all organizational facets, underpinning the company’s ability to achieve its objectives and maintain competitive advantage in the market.
Transformational leadership was introduced by James McGregor Burns (Burns 1978) and developed by Bernard Bass (B. Bass 1985). Burns (1978) developed transactional and transformational leadership, where the former is a contractual process in which leaders provide rewards in exchange for employees’ performance, and the latter is an influence process aimed at generating greater motivation by articulating an inspiring vision. (Ngoc Khuong, Thanh Tung and Hoang Quoc 2022) Concept of transformational leadership lead to increasing the authority of leaders to inspire and motivate their followers and employees and ultimately lead to the preference of the organization’s interests over their own self-interests. Transformational leadership is characterized by four main components: idealized influence, inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation, and individualized consideration (Bass and Riggio 2006). As organizations grow, there is an increasing need for trained leaders who can overcome complex challenges and inspire their teams to achieve outstanding results. Transformational leadership has proven to be an effective model in various contexts, fostering an environment of trust, innovation, and high performance. (Burns 1978)
Transformational leadership is an influence process in which leaders catalyze greater motivation from followers by articulating an inspiring vision. (Ngoc Khuong, Thanh Tung and Hoang Quoc 2022, 12) As earlier mentioned transformational leadership, introduced by James MacGregor Burns and expanded by Bernard M. Bass, is defined by four key components, often referred to as the “Four I’s” (Ellen 2016, 2-3):
- Idealized Influence: Leaders act as role models, gaining the trust and respect of employees.
- Inspirational Motivation: Leaders articulate a clear vision that is appealing and inspiring to employees
- Intellectual Stimulation: Leaders encourage innovation and creativity by challenging the status quo and encouraging employees to explore new ways of doing things
- Individualized Consideration: Leaders provide personalized encouragement and support to each employee, recognizing their unique needs and aspirations
Problem Statement
Despite extensive research on transformational leadership, there is a significant gap in understanding its specific impact in mid-sized technology organizations. Technology organizations operate in very dynamic and competitive environments. Due to this dynamic and competition in this field, the need for research on the impact of transformational leadership on the performance and creativity of employees in such organizations has increased. The specific challenges that technology organizations face, such as rapid technological advances, huge competition in the market, and the constant need for innovation, require transformational leadership that not only covers these challenges but also increases the performance and innovation of employees.
Importance of the Study
This study is significant in that it provides a detailed examination of the impact of transformational leadership on employee performance and motivation within medium-sized technology organizations. The study presents a robust evidence base demonstrating that transformational leadership practices enhance productivity and job satisfaction, and foster intrinsic motivation and organizational commitment. This is a crucial finding for tech organizations seeking to maintain competitive advantage and innovation in a rapidly evolving industry. The findings highlight the need for leadership development programs and the strategic allocation of resources towards fostering transformational leadership, which ultimately drives sustained organizational success and employee well-being.
Theoretical Framework
Transformational leadership theory posits that transformational leaders can achieve superior results by transforming their followers’ values, goals, and aspirations. This theory contrasts with transactional leadership, which focuses on routine activities and rewards or punishments based on performance outcomes. (FRED OCHIENG and LUCY 2000) Empirical studies have shown that transformational leadership positively affects a wide range of organizational outcomes, including employee satisfaction, commitment, and performance.
Survey Results
The survey was conducted among 41 employees in medium-sized tech organizations, assessing various aspects of transformational leadership and its impact on employee performance and motivation. All survey participants were aged between 25 and 54 years. Specifically, 46.3% were aged 25-34 years, 39% were aged 35-43 years, and 14.6% were aged 45-54 years, and 58% were female. In the survey, participants held a variety of roles. In descending order of quantity, the roles were: Software Developer, Project Manager, Quality Assurance, Systems Analyst, IT Support, Brand Manager, HR Manager, and Bioinformatician.
In the survey, 65.9% of participants rated their performance in the past year as good, while 34.1% rated it as excellent. In this survey, 24.4% of participants reported feeling extremely motivated in their current job, 48.8% felt very motivated, 24.4% felt moderately motivated, and 2.4% felt slightly motivated.
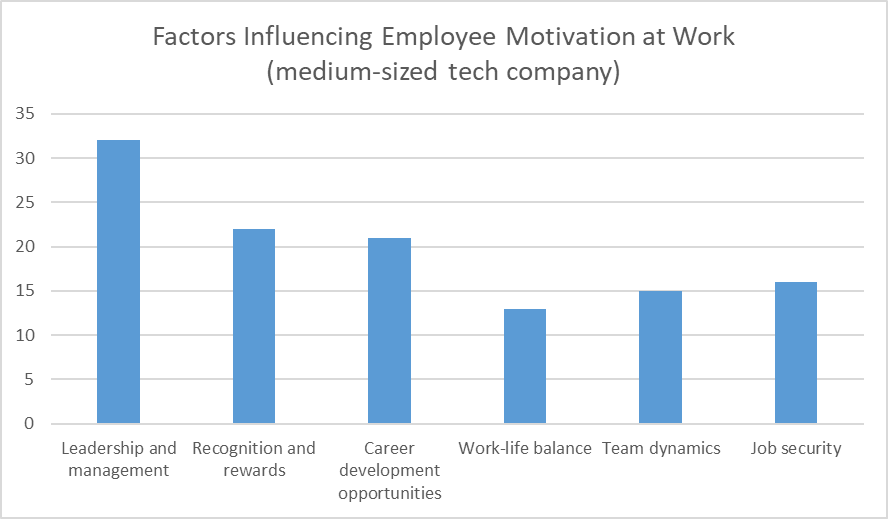
Also, we examined the factors that most influence employee motivation at work. The findings indicated that leadership and management were the most influential factors, followed by recognition and rewards. Career development opportunities and job security were also significant. Additionally, team dynamics and work-life balance were identified as important motivational factors by the participants.
Analysis and Discussion
The survey results indicate that transformational leadership practices, such as encouraging innovative thinking and problem-solving, also acting as a role model and recognizing contributions, significantly enhance employee productivity and the quality of work. Also F. Ochieng and et al. believe (FRED OCHIENG and LUCY 2000) encourage employees to take ownership of their tasks and strive for excellence.
High ratings for individualized consideration and inspirational motivation suggest that transformational leaders effectively increase job satisfaction and loyalty among employees. This aligns with research showing that employees who feel valued and supported are more likely to be committed to their organization (Ellen 2016).
The survey findings highlight that transformational leadership fosters intrinsic motivation and empowerment. This aligns with research of F. Ocjieng (FRED OCHIENG and LUCY 2000) which proves that employees are motivated by leaders who align organizational goals with their personal values and aspirations, which in turn enhances their commitment and performance.
Conclusion and recommendations
Transformational leadership has a deep impact on employee performance and motivation in medium-sized tech organizations. By development an inspiring vision, encouraging innovation, and providing individualized support, transformational leaders can drive superior organizational outcomes. As tech organizations continue to grow, acceptance of transformational leadership can be a key differentiator in achieving sustained success and employee satisfaction. Below are the achievements of this article that can be used for the transformational management of companies in the field of technology.
- Leadership Training: It is recommended that managers participate in training programs to develop transformational leadership skills, because managers and leaders have a crucial role in the performance and creativity of employees. Therefore, it is recommended that they acquire enough knowledge for transformational leadership in the team by studying and training.
- Employee Feedback Systems: Implement strong feedback mechanisms that allow continuous assessment and improvement of leadership effectiveness. Regular feedback from employees can help leaders understand their impact and make necessary adjustments. This assessment can be at the end of each project, or in the tech team which owns the product period can be monthly.
- Recognition and Reward Programs: Establish programs that recognize and reward innovative contributions and high performance. Based on results of the survey rewards are the second most important factor for employees. Recognition should be timely and meaningful to motivate employees and reinforce positive behaviors.
- Continuous Learning Culture: Develop a culture that values continuous learning and development. In the survey having time for work on self-development and learning new topics is mentioned as an important factor. Also, since the speed of knowledge growth is very high in tech companies, it is recommended to provide employees with enough time to learn new technologies and even encourage them to do so. Encourage employees to pursue further education and skills development, and provide resources and opportunities for them to do so. This not only enhances individual growth but also contributes to the organization’s overall innovation and adaptability.
References
- Bass, B. M., and R. E. Riggio. 2006. Transformational Leadership (2nd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Bass, Bernard M. 1985. Leadership and performance beyond expectations. New York: The Free Press.
- Burns, J. M. 1978. Leadership. New York: Harper & Row.
- Ellen, B. Parker. 2016. “Transformational Leadership.” In Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance, by Ali Farazmand, 1-4. Springer International Publishing.
- FRED OCHIENG, Walumbwa, and A. OJODE LUCY . 2000. “Gender stereotype and instructors’ leadership behavior: Transformational and transactional leadership.” Midwest Academy of Management Annual Conference. Chicago, IL.: Vol. 30.
- Ngoc Khuong, Mai, Do Thanh Tung, and Thai Hoang Quoc. 2022. “Review of Empirical Research on Leadership and Firm Performance.” Sage Open 3-12.
Appendix No. 1: Survey on Transformational Leadership: Assessing its Impact on Employee Performance and Motivation
Dear Participant,
We are conducting a survey to understand the impact of transformational leadership on employee performance and motivation within medium-sized tech organizations. Your feedback is invaluable in helping us assess the effectiveness of leadership practices and their influence on your work experience.
The survey is anonymous and will take approximately 10-15 minutes to complete. Thank you for your participation!
Section 1: Demographics
- What is your age?
- Under 25
- 25-34
- 35-44
- 45-54
- 55 and above
- What is your gender?
- Male
- Female
- Non-binary/Third gender
- Prefer not to say
- What is your job role?
- Software Developer
- Project Manager
- Quality Assurance
- Systems Analyst
- IT Support
- Other (please specify)
- How long have you been with your current organization?
- Less than 1 year
- 1-3 years
- 4-6 years
- 7-10 years
- More than 10 years
Section 2: Leadership Assessment
- How frequently does your immediate supervisor engage in the following behaviors? (Rate on a scale of 1 to 5, where 1 = Never, 5 = Always)
- Acts as a role model for employees.
- Articulates a clear and inspiring vision for the future.
- Encourages innovative thinking and problem-solving.
- Provides personalized support and mentoring.
- Recognizes and rewards employees’ contributions.
- To what extent do you agree with the following statements? (Rate on a scale of 1 to 5, where 1 = Strongly Disagree, 5 = Strongly Agree)
- My supervisor inspires me to perform my best.
- I feel motivated to contribute to the organization’s goals.
- I have opportunities to develop my skills and advance my career.
- My supervisor values my input and ideas.
- I feel a strong sense of loyalty to my organization.
Section 3: Performance and Motivation
- How would you rate your overall job performance over the past year?
- Excellent
- Good
- Average
- Below Average
- Poor
- How motivated are you to go above and beyond in your current role?
- Extremely motivated
- Very motivated
- Moderately motivated
- Slightly motivated
- Not at all motivated
- What factors most influence your motivation at work? (Select all that apply)
- Leadership and management
- Recognition and rewards
- Career development opportunities
- Work-life balance
- Team dynamics
- Job security
- Other (please specify)
- In what ways has your supervisor influenced your performance and motivation? (Open-ended)
Section 4: Organizational Culture
- To what extent do you agree with the following statements about your organization? (Rate on a scale of 1 to 5, where 1 = Strongly Disagree, 5 = Strongly Agree)
- The organization promotes a culture of continuous improvement.
- There is a strong sense of teamwork and collaboration.
- Employees are encouraged to take initiative and be creative.
- The organization values and supports employee development.
- Communication within the organization is transparent and effective.
- What improvements, if any, would you suggest for enhancing leadership practices in your organization? (Open-ended)
Appendix No. 2: Reliability Test of Survey
In order to analyze and check the validity and reliability of the survey, Cronbach’s Alpha and Anova tests were used, which are the most useful tools and instruments of survey reliability. All the results are presented in the following tables.
Table 1: Case Processing Summary
| Case Processing Summary | |||
| N | % | ||
| Cases | Valid | 41 | 100.0 |
| Excludeda | 0 | .0 | |
| Total | 41 | 100.0 | |
Table 2: Statistics summary of indicators
| Summary Item Statistics | ||||||
| Mean | Min | Max | Range | Max/ Min | Variance | |
| Item Means | 4.116 | 3.683 | 4.634 | .951 | 1.258 | .055 |
| Item Variances | .661 | .230 | .860 | .629 | 3.730 | .020 |
| Inter-Item Covariances | .435 | -.032 | .703 | .735 | -21.755 | .027 |
| Inter-Item Correlations | .650 | -.090 | .946 | 1.036 | -10.517 | .043 |
Table 3: Reliability Statistics of Survey
| Reliability Statistics | ||
| Cronbach’s Alpha | Cronbach’s Alpha Based on Standardized Items | N of Items |
| 0.970 | 0.969 | 17 |
The table of reliability statistics of the survey, was done by using Cronbach’s alpha show, the reliability statistics highlight a Cronbach’s alpha value of 0.970, which indicates excellent and acceptable consistency for the survey items. This value suggests that the survey items and indicators are highly correlated and effectively measure the underlying concepts. It should be noted that the reliability analysis also includes 17 indicators (the nominal and qualitative criteria and open-ended questions were not included) and the Cronbach’s alpha based on normalized standardized indicators is 0.969, further confirming and demonstrating the robustness and validity of the survey instruments.
These results indicate that the structure and content of the survey was very well designed and conducted, providing reliable data that can be confidently used for further research in the field of management and transformational leadership impact on employee outcomes. Therefore, the findings can be generalized to other communities and organizations.
